What is Contraception?
Contraception is a device or medication that is used to prevent unplanned pregnancies. Unprotected sexual intercourse can result in unwanted pregnancy and may lead to abortion. Thus, contraception or birth control methods are used to avoid pregnancy which may end up in abortion.
There are many different methods of birth control and each one is different in its mode of action and efficacy. Each one has its advantages and disadvantages, hence women can choose the best method based on their unique needs and requirements.
Birth Control in Singapore
One of the most common birth control methods used in Singapore is condoms. While the contraceptive failure rate is highest with condoms among all other methods (because when and how the condom is put on will significantly impact the protective function of it. There is also a chance of the condom tearing during intercourse), they are the only method that gives protection against sexually transmitted infections (STIs). Condoms are conveniently available at any convenience store or supermarket; whilst the other methods. require a prescription from a gynaecologist in Singapore after a proper consultation is made. The prices might vary depending on where you see your gynae (public vs private hospitals).
Types of Birth Control Methods
There is a wide array of contraceptive options available in Singapore, though they can be divided into 2 major categories.
Contraceptive Effect |
Temporary (Reversible) |
Permanent |
|---|---|---|
Method |
Short-acting
Long-acting
|
Tubal Ligation |
Reversible Contraception
I. Short-acting
a. Oral Contraceptive Pills (aka Birth Control Pills)
How do Birth Control Pills (BCPs) work?
In a natural menstrual cycle, the levels of female hormones i.e. estrogen and progesterone will rise and fall accordingly to result in ovulation. The progesterone will also help support implantation of the egg if it is fertilized by the sperm. BCPs are oral tablets that contain synthetic versions of these female reproductive hormones either singly or as a combination. They are taken daily for 3 weeks of the menstrual cycle starting from Day 1 or Day 5 of menstruation, as advised by your doctor, and stopped for 1 week to allow menstruation to occur. As a result, a steady hormonal level is maintained, which in turn prevents ovulation from taking place. In addition, it causes thickening of the cervical mucus to prevent the sperm from reaching the egg and also changes the uterine lining to prevent implantation should fertilization of the egg still take place.
How effective are BCPs?
It is generally about 98-99% effective (NHS UK), provided it is taken strictly as instructed.
Advantages of BCPs
BCPs are suitable for most women, provided they are committed to taking the pills regularly. They also help women who have irregular menstrual cycles regulate their menstruation (menstruation happens during the 1-week gap of no pills in a 28-day course).
Disadvantages of BCPs
They cannot be taken by breastfeeding mothers and those with medical problems such as liver disorders, high blood pressure and women older than 40 years. They must be taken strictly as instructed to ensure contraceptive efficacy. Missing a pill for a day would require you to check with you gynae on the next steps.
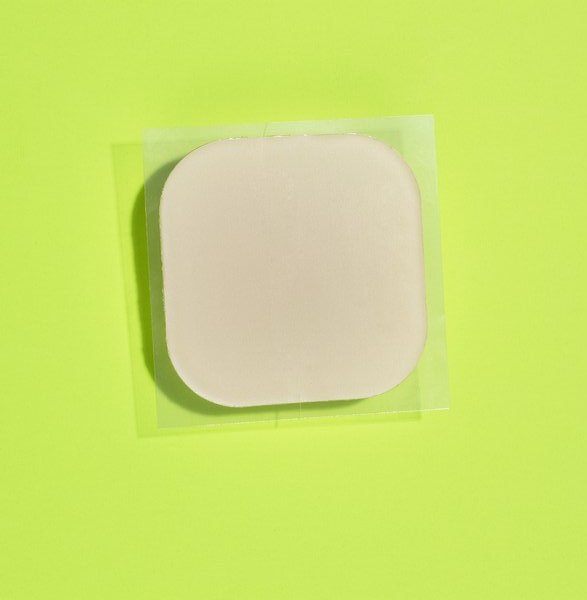
b. Birth Control Patch
How does the Birth Control Patch work?
The birth control patch is an adhesive that is stuck on the skin, where it releases hormones gradually over time to prevent ovulation, thicken cervical mucus and change the uterine lining. The hormones progestin and estrogen would be absorbed through the skin.
Each patch lasts for exactly a week; therefore, it should be changed every week on the same day for the first 3 weeks. This is then followed by a rest period of one week, to allow menstruation to take place. The patch is put on Day 1 of your menstrual cycle.
How effective is the Birth Control Patch?
It is 91-99% effective (NHS UK).
Advantages of the Patch
Women may experience less acne, a lighter menstrual flow and less menstrual cramps. It is also a very convenient option for women.
Disadvantages of the Patch
It can get uncomfortable to wear and some women may even experience skin irritation. Some negative side effects include nausea, tender breasts and in some instances, bleeding between periods. Some of the side effects do go away once your body gets used to the patch after about 2-3 months.
c. Contraceptive Injection
How does the Contraceptive Injection Work?
It is an injection of long-acting progesterone (called Depo Provera) that prevents ovulation from taking place and thickens the cervical mucus which prevents sperm from meeting the egg.
How Effective is the Contraceptive Injection?
It is about 98% effective (NHS UK) provided you go for your injection regularly.
Advantages of the Contraceptive Injection
You will only need to go for your injection 4 times a year i.e. every 12 weeks. The injection also reduces the risk of developing endometrial cancer.
Disadvantages of the Contraceptive Injection
Some women may not get menstruation at all, while 1/3 get irregular staining on and off and 1/3 get regular menstruation. Some women experience weight gain as their bodies adjust to the injection for the first few months.
II. Long-acting
a. Implanon: Contraceptive Implant
How does the Contraceptive Implant Work?
Contraceptive implants are devices that can be injected under the skin. They contain hormones such as progesterone, which is released from the implant slowly over time, to exert the contraceptive effect by preventing ovulation from taking place.
How Effective is the Contraceptive Implant?
It is 99% effective (NHS UK).
Advantages of Contraceptive Implants
It can last for as long as 3 years and is convenient with no need for annual checkups. Some women may also find that they get lighter periods or do not get their period at all with these implants.
Disadvantages of Contraceptive Implants
Insertion of the implant involves a small 1 cm cut on the skin of the arm, to insert the implant, which can cause mild scarring. Other side effects include weight gain, headaches, tender breasts and nausea. Another more common side effect is irregular bleeding. Also, if the woman gains too much weight after 3 years from the point of insertion, removal of the implant may be more difficult.
b. Intra-Uterine Contraceptive Devices (IUCDs)
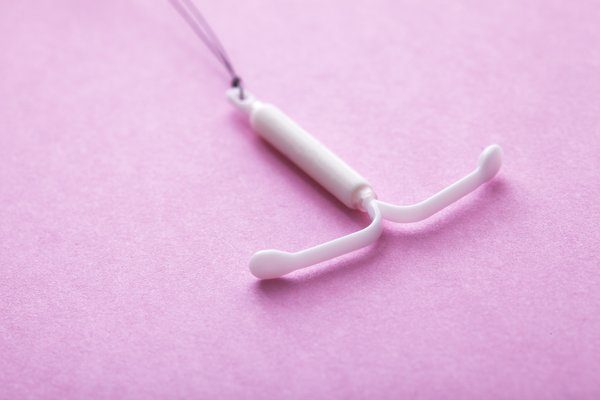
Hormonal IUCD
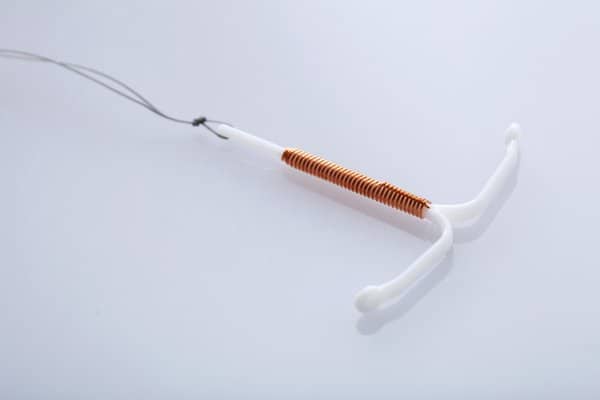
Copper IUCD
IUCDs are tiny contraceptive devices, measuring approximately 2cm, that are inserted within the uterus to prevent pregnancy from taking place. These devices can be easily inserted in the gynecologist’s clinic in a short 15-30min procedure. It is needs to be inserted on Day 5 of menstruation. The slight discomfort associated with the insertion procedure can be reduced by having the procedure done during your menstruation, as that is when your cervix is dilated. Oral painkillers can also be given to help with pain relief.
Hormonal IUCD |
Non-hormonal (Copper) IUCD |
|
|---|---|---|
How does it work? |
|
|
How effective is it? |
99% effective (NHS UK) – more effective than sterilization |
99% effective (NHS UK) |
Advantages |
|
|
Disadvantages |
|
|
Permanent Contraception – Tubal Ligation
How does ligation work?
Ligation involves a minor surgery which can be done as a day surgery procedure. The fallopian tubes in a woman can be cut and ligated or clips can be applied. Both are equally effective. This ensures the eggs cannot travel to the uterus anymore.
Men can have sterilization in a similar fashion. It is also a day surgery and the procedure is comparatively less risky than the fallopian tube ligation for women.
How effective is ligation?
It is considered to be 99.5% (NHS UK).
Advantages of ligation
It is a permanent method thus when it is done, you do not need to worry about having unprotected sexual intercourse.
Disadvantages of ligation
As it is an irreversible method, it will not be possible to have another baby in future. Also, it is a surgical procedure and is associated with surgical risks. There is still a small risk of contraceptive failure, 0.5%, meaning 1 in 200 may end up with pregnancy. This pregnancy may be outside the womb (ectopic pregnancy), which can be life-threatening. If you are considering this option, have a detailed discussion with your gynaecologist.
What about the morning-after pill?
This is a birth control measure used after unprotected sexual intercourse to prevent pregnancy. It works by preventing implantation and is given in a single dose.
How effective is the morning-after pill?
It is generally about 98% effective, but it can only be taken up to 72 hours after sexual intercourse.
Do I need a doctor’s prescription for the morning-after pill?
Yes. The morning-after pill needs to be prescribed by your gynae. You would need to see the gynae and not send your partner to pick it up on your behalf. The reason is that gynaecologists need to check you before you can take the medication.
Can it be taken frequently?
This is only for emergency purposes; if taken frequently, it can cause menstrual irregularities.
Thus, it is advisable to use other contraceptive measures.
Contraception is important if you are not ready to have children yet. Consult your gynaecologist about the options available as he/she will take into consideration factors like your medical history, family planning, pre-existing gynaecological issues and your lifestyle to help you choose the most appropriate method of birth control.
Book an appointment with our gynae in Singapore at SMG Women’s Health if you are considering contraception.